Scientific Highlights
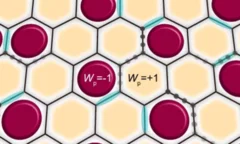
Kondo screening in a Majorana metal
Kondo impurities provide a nontrivial probe to unravel the character of the excitations of a quantum spin liquid. In the S = 1/2 Kitaev model on the honeycomb lattice, Kondo impurities embedded in the spin-liquid host can be screened by itinerant Majorana fermions via gauge-flux binding. Here, we report experimental signatures of metallic-like Kondo screening at intermediate temperatures in the Kitaev honeycomb material α-RuCl3 with dilute Cr3+ (S = 3/2) impurities.
Sustainable Group-IV Active Photonics Research Sinergia Project granted
We are excited to announce that our joint Sinergia Project: Sustainable Group-IV Active Photonics Research (SUGAR) has been approved for funding by the SNSF and will start in the spring of 2024. SUGAR is an interdisciplinary project that aims to develop a more sustainable photonics platform, based on group IV elements (Si, Ge, Sn). The proposal emphasizes sustainability throughout the entire device life-cycle, incorporating life cycle assessment (LCA) from extraction to end-of-life.
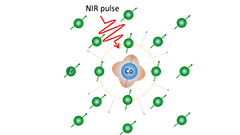
Mechanism For All-Optical Magnetization Switching
X-rays reveal a non-collinear magnetic state as the base for all-optical magnetization switching.
New Nat. Rev. Phys. publication: A “gold standard” for computational materials science codes
A large consortium of scientists, coordinated by PSI researchers in the LMS laboratory, led the most comprehensive verification effort so far on computer codes for materials simulations, providing their colleagues with a reference dataset and a set of guidelines for assessing and improving existing and future codes.
A gold standard for computational materials science codes
The most comprehensive verification effort so far on computer codes for materials simulations.
Park Innovaare Cleanroom Name is: PICO
We are happy to announce that the new Cleanroom Name in the Park Innovaare will be PICO = Park Innovaare Cleanroom for Optics and innovation.
Next Step – we will work on a Logo (ideas welcome), together with PiA.
The winner of the naming contest: Helmut Schift
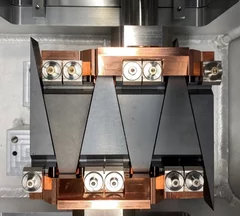
A more efficient degrader for proton therapy
At PSI’s Center for Proton Therapy (CPT), protons are used to treat cancerous tumours in a highly targeted way that spares healthy tissue as much as possible. This is the result of the characteristic way in which charged particles interact with matter, so that a beam of protons deposits most of its energy at a certain depth in a material depending on the energy and the composition of the material. The dedicated medical cyclotron COMET accelerates protons to an energy of 250 MeV, which then have to be "slowed down" so that the energy matches the depth of the tumour to be treated.
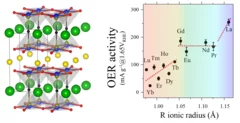
Cobalt-free layered perovskites RBaCuFeO5+d (R = 4f lanthanide) as electrocatalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction
Co oxides with perovskite-related structure are particularly promising, cost-effective OER catalysts. However, the increasing Co demand by the battery industry is pushing the search for Co-free alternatives. Here we investigate the potential of the Co-free layered perovskite family RBaCuFeO5+δ (R = 4f lanthanide), where we identify the critical structural and electronic variables leading to high OER catalytical performance. The employed methodology, based in the use of advanced neutron and X-ray synchrotron techniques combined with ab initio DFT calculations allowed to reveal LaBaCuFeO5+δ as new, promising Co-free electroctalyst. Moreover, we could show that this material can be industrially produced in nanocrystalline form. We believe that the reported results and methodology may contribute to the implementation of new technologies aimed to generate energy with lower carbon emissions, and can also inspire the scientific community in their search of other Co-free materials with good OER electrocatalytical properties.
Additive manufacturing of alloys with programmable microstructure and properties
Using laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) technology, we devise special processing strategies to ‘program’ the thermal stability of the as-printed alloy, such that it is possible to decide, a priori, how the material’s microstructure will evolve upon heat treatment
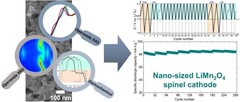
Understanding the (de-)lithiation mechanism of nano-sized LiMn2O4 allows achieving long-term cycling stability
We report an in-depth investigation of the local atomic geometry, electronic and crystallographic structure evolution of nano-sized LiMn2O4 using operando XAS and XRD to shed light on (de-)lithiation mechanism when cycled in wide voltage range of 2.0 to 4.3 V vs Li+/Li. Leveraging on these findings, a novel electrochemical cycling protocol, with periodic deep discharge, yields superior electrochemical performance cycled in the range of 3.3 to 4.3 V exhibiting an excellent structure cyclability and an unprecedented increase in the specific capacity upon long cycling.