Search
Oxygen Evolution Reaction Activity and Underlying Mechanism of Perovskite Electrocatalysts at Different pH
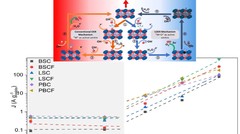
PSI researchers have studied the how the electrolyte pH values influence the oxygen evolution reaction (OER) activity and stability of different promising perovskite oxide catalysts for application as anodic electrodes in alkaline water electrolyzers. The OER activity and stability decreased decreasing the electrolyte pH values. By combining electrochemical studies and operando X-ray absorption spectroscopy measurements, it has been suggested that different reaction mechanisms dominate in alkaline and near-neutral electrolyte pH region.
Surface segregation acts as surface engineering for the oxygen evolution reaction on perovskite oxides in alkaline media
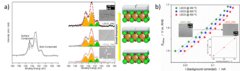
PSI researchers have studied the influence of surface segregation on the oxygen evolution reaction (OER) activity for the, La0.2Sr0.8CoO3-d (LSCO) perovskite, one of the most active perovskite towards the OER in alkaline electrolyte. It has been found that the higher the perovskite synthesis temperature the more strontium segregation occurs on the surface. However, the segregated strontium compounds are soluble in water and they are easily removed when the surface of the electrode is in contact with the electrolyte, leading to the exposure of cobalt enriched layers very active for the OER.
Toward better motors with X-ray light
Making Switzerland's road traffic fit for the future calls for research, first and foremost. In the large-scale research facilities of PSI, chemists and engineers are investigating how to improve the efficiency of motors and reduce their emissions.
Publications 2009
Electrochemistry Laboratory (LEC)
Energy transition
Topic Overview
Energy and Climate
Topic Overview
Première: visualiser la glace dans les piles à combustible
A l’aide d’une méthode novatrice, des chercheurs de l’Institut Paul Scherrer (PSI) ont réussi une première : visualiser directement la répartition de la glace et de l’eau liquide dans une pile à combustible à hydrogène. Pour distinguer de manière très fiable les zones où se trouve de l’eau liquide de celles où se trouve de la glace, cette nouvelle technique d’imagerie utilise successivement deux faisceaux de neutrons, dotés chacun d’une énergie différente. La méthode ouvre ainsi une perspective : la possibilité d’analyser l’un des principaux problèmes lié à l’utilisation de piles à combustible pour la propulsion de véhicules. La glace peut en effet boucher les pores dans les piles, et ainsi entraver leur fonctionnement. Les scientifiques du PSI ont publié leurs résultats le 16 juin 2014, dans la revue «Physical Review Letters».
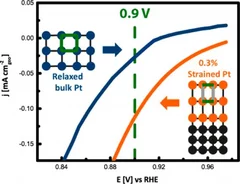
Investigating the Role of Strain toward the Oxygen Reduction Activity on Model Thin Film Pt Catalysts
Environmentally friendly energy conversion devices such as fuel cells are becoming more and more attractive. However, major impediments to large-scale application still arise on the material side, related to the cost and poor performance of the cathode catalyst. State-of-the-art electrocatalysts are all Pt-based materials, suffering from poor electrochemical oxygen reduction kinetics.
Des carburants verts pour l’aviation
Le PSI et l’Empa veulent développer conjointement une méthode pour produire du kérosène à partir de ressources renouvelables.
Publications 2012
Electrochemistry Laboratory (LEC)
Natasha joined PSI in September 2021 as a PhD candidate in the Electrocatalysis and Interfaces Group under the supervision of Dr Emiliana Fabbri and Prof. Thomas Schmidt.
Past Publications
Thin Films and Interfaces
List of Publications
Thin-disk laser pump schemes for large number of passes and moderate pump source quality K. Schuhmann, T.W. Hänsch, K. Kirch, A. Knecht, F. Kottmann, F. Nez, R. Pohl, D. Taqqu, and A. Antognini. arXiv:1509.07891 (2015). Experiments towards resolving the proton charge radius puzzle
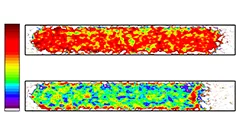
First direct observation of the oxygen transport in polymer electrolyte water electrolysis
PSI researchers have developed a new methodology for studying the complex transport processes in polymer electrolyte water electrolysis (PEWE). Using advanced operando X-ray tomographic microscopy, we were able to observe for the first time the formation of oxygen pathways in the porous transport layer, in three dimensions. Understanding oxygen transport is crucial for improving PEWE technology and this work provides precious insights for the design of future, better-performing PEWE cells.