Scientific Highlights
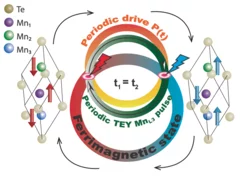
Efficient magnetic switching in a correlated spin glass
The interplay between spin-orbit interaction and magnetic order is one of the most active research fields in condensed matter physics and drives the search for materials with novel, and tunable, magnetic and spin properties. Here we report on a variety of unique and unexpected observations in thin multiferroic Ge1−xMnxTe films.
Insights into radical induced degradation of anion exchange membrane constituents
Electrochemical energy conversion devices, such as fuel cells and electrolyzers, using an anion exchange membrane (AEM) operating in the alkaline regime offer the prospect of the use of non-noble metal electrocatalysts and lower-cost cell construction materials. The wide-spread application of electrochemical cells with AEMs has been largely limited by the low chemical stability of the material. AEM degradation is triggered by i) nucleophilic attack by OH−, and ii) by reaction with free radicals formed during cell operation. Whereas the alkaline stability of AEMs has been greatly increased over the last 10 years, the understanding of mechanisms of radical induced degradation is limited. In this study, we have addressed this topic for the first time.
Direct observation of topological magnon polarons in a multiferroic material
Magnon polarons are novel elementary excitations possessing hybrid magnonic and phononic signatures, and are responsible for many exotic spintronic and magnonic phenomena. Despite long-term sustained experimental efforts in chasing for magnon polarons, direct spectroscopic evidence of their existence is hardly observed. Here, we report the direct observation of magnon polarons using neutron spectroscopy on a multiferroic Fe2Mo3O8 possessing strong magnon-phonon coupling.
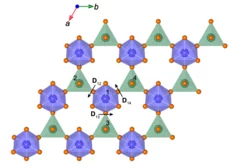
Complete field-induced spectral response of the spin-1/2 triangular-lattice antiferromagnet CsYbSe2
Fifty years after Anderson’s resonating valence-bond proposal, the spin-1/2 triangular-lattice Heisenberg antiferromagnet (TLHAF) remains the ultimate platform to explore highly entangled quantum spin states in proximity to magnetic order. Yb-based delafossites are ideal candidate TLHAF materials, which allow experimental access to the full range of applied in-plane magnetic fields. We perform a systematic neutron scattering study of CsYbSe2, first proving the Heisenberg character of the interactions and quantifying the second-neighbor coupling.
Biffo the fish: BiFeO3 nanoplate wins the Magnetism Art Competition at JEMS 2023 in Madrid
Dr. Tim A. Butcher from the Microspectroscopy group was awarded the first prize in the "Art in Magnetism" competition of the JEMS 2023 conference with his contribution "Biffo", obtained from a ptychography image of a BiFeO3 nanoplate.
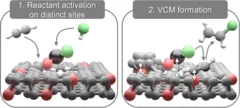
Evidence of bifunctionality of carbons and metal atoms in catalyzed acetylene hydrochlorination
Carbon supports are ubiquitous components of heterogeneous catalysts for acetylene hydrochlorination to vinyl chloride, from commercial mercury-based systems to more sustainable metal single-atom alternatives. Their potential co-catalytic role has long been postulated but never unequivocally demonstrated. Herein, combining operando X-ray absorption spectroscopy with other spectroscopic and kinetic analyses, we evidence the bifunctionality of carbons and metal sites (Pt, Au, Ru) in the acetylene hydrochlorination catalytic cycle.
Thank You SLS
Our beamline scientists look back on 22 years of brilliant science made possible by the Swiss Light Source SLS.
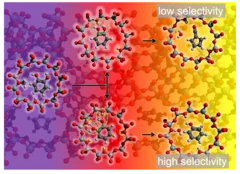
Unveiling the reaction mechanism shines light on the selectivity increase in catalytic processes
Increasing the selectivity of a chemical process through rational catalyst design is the Holy Grail of heterogeneous catalysis. Researchers at PSI and ETH Zürich showcase how revealing hidden steps in reaction pathways can steer processes towards preferred products, as demonstrated in a study focused on biomass valorization.
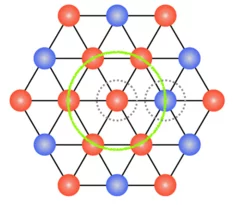
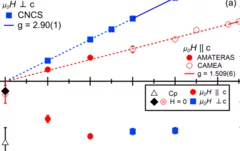
Field-tuned quantum renormalization of spin dynamics in the honeycomb lattice Heisenberg antiferromagnet YbCl3
The basis for our understanding of quantum magnetism has been the study of elegantly simple model systems. However, even for the antiferromagnetic honeycomb lattice with isotropic spin interactions – one of the simplest model systems – a detailed understanding of quantum effects is still lacking. Here, using inelastic neutron scattering measurements of the honeycomb lattice material YbCl3, we elucidate how quantum effects renormalize ...
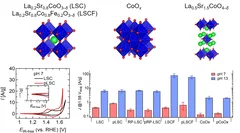
Improving the oxygen evolution reaction activity of Co-based oxides by phosphate functionalization
Our findings disclose that P-functionalization successfully enhances the oxygen evolution reaction (OER) activity of different cobalt-based catalysts (namely, La0.2Sr0.8CoO3–δ, La0.2Sr0.8Co0.8Fe0.2O3–δ, and CoOx) at near-neutral pHs and that both phosphate ion assistance in the OER mechanism and catalyst Co oxidation state can play a role in the enhanced OER activity.