Scientific Highlights
Additive manufacturing of alloys with programmable microstructure and properties
Using laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) technology, we devise special processing strategies to ‘program’ the thermal stability of the as-printed alloy, such that it is possible to decide, a priori, how the material’s microstructure will evolve upon heat treatment
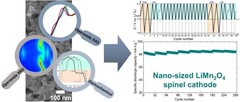
Understanding the (de-)lithiation mechanism of nano-sized LiMn2O4 allows achieving long-term cycling stability
We report an in-depth investigation of the local atomic geometry, electronic and crystallographic structure evolution of nano-sized LiMn2O4 using operando XAS and XRD to shed light on (de-)lithiation mechanism when cycled in wide voltage range of 2.0 to 4.3 V vs Li+/Li. Leveraging on these findings, a novel electrochemical cycling protocol, with periodic deep discharge, yields superior electrochemical performance cycled in the range of 3.3 to 4.3 V exhibiting an excellent structure cyclability and an unprecedented increase in the specific capacity upon long cycling.
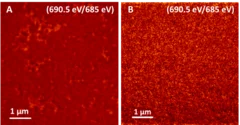
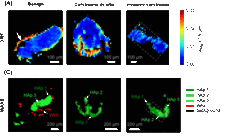
TEY-STXM confirms homogeneous doping of nanoparticles for non-fullerene organic solar cells
One of the challenges in modern research on the fabrication of non-fullerene acceptor based organic solar cells is the availability of very efficient hole transport layers (HTLs). A new approach that avoids mutual solubility issues is to deposit the HTL from a suspension of doped organic nanoparticles. Surface-sensitive TEY-STXM measurements at the PolLux beamline characterised the homogeneity of the dopant in the nanoparticles and develop efficient nanoparticle HTL materials for organic solar cells.
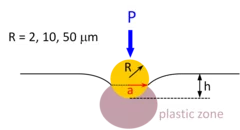
Investigations of the irradiation hardening on a ferritic model alloy from spherical nano-indentations
The objective of this project was to determine the contribution from a variety of obstacles to moving dislocations to the nano-indentation stress necessary to initiate plastic flow. The obstacles are characterized by different length scales. Among these characteristic lengths, there are those associated with the material microstructure such as grain size, dislocations density, irradiation-induced defects, and those related to the size of the plastic zone beneath the indenter, or equivalently to the size of the indent. Thus, we can classify the size effects into two categories: structural size effect and indentation size effect (ISE). The underlying idea is to quantify and separate these two effects on the unirradiated material first to be able to properly isolate the contribution of the irradiation defect on the measured hardness from the tests on irradiated materials.
Using quantum computers already today
Analogue quantum computers make ultrafast chemical reactions observable.
Open Quantum Institute launch
Dr. Cornelius Hempel, head of the Ion Trap Quantum Computation group at LNQ’s ETHZ-PSI Quantum Computing Hub, spoke to SRF to explain how quantum computers work and how future versions of these devices can be used to solve some of the big problems of our time.
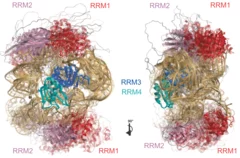
Integrative solution structure of PTBP1-IRES complex reveals strong compaction and ordering with residual conformational flexibility
RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) are crucial regulators of gene expression, often composed of defined domains interspersed with flexible, intrinsically disordered regions. Determining the structure of ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complexes involving such RBPs necessitates integrative structural modeling due to their lack of a single stable state. In this study, we integrate magnetic resonance, mass spectrometry, and small-angle scattering data to determine the solution structure of ...
Whitlockite in mammary microcalcifications is not associated with breast cancer
Microcalcifications, small deposits of calcium-containing minerals that form in breast tissue, are often, but not always, a warning sign of breast cancer. The relationship between microcalcifications and cancer has not been fully understood thus far. Researchers discovered now that the relationship between microcalcifications and tumors seems to be linked to the presence of a particular mineral called whitlockite, which is rich in magnesium and is found in microcalcifications only in the absence of tumors.
LXN post-doctoral researcher Dr. Prajith Karadan wins Best Poster Award at MNE conference 2023, Berlin
The MNE (Micro and Nano Engineering) conference is a prestigious annual event that serves as a global platform for experts, researchers, and innovators in the field of micro and nanotechnology. This conference brings together leading minds from academia and industry to share cutting-edge research, exchange ideas, and explore emerging trends and breakthroughs in the world of micro and nanoengineering.
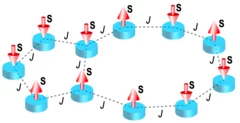
Electrically programmable magnetic coupling in an Ising network exploiting solid-state ionic gating
Two-dimensional arrays of magnetically coupled nanomagnets provide a mesoscopic platform for exploring collective phenomena as well as realizing a broad range of spintronic devices. In particular, the magnetic coupling plays a critical role in determining the nature of the cooperative behavior and providing new functionalities in nanomagnet-based devices. Here, we create coupled Ising-like nanomagnets ...