NUM division - Publication Highlights
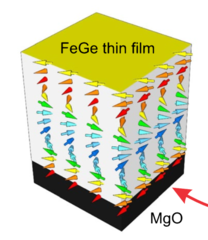
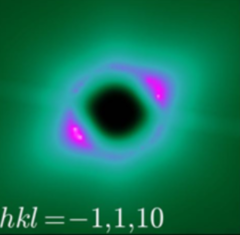
Room-temperature helimagnetism in FeGe thin films
Chiral magnets are promising materials for the realisation of high-density and low-power spintronic memory devices. For these future applications, a key requirement is the synthesis of appropriate materials in the form of thin films ordering well above room temperature. Driven by the Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction, the cubic compound FeGe exhibits helimagnetism with a relatively high transition temperature of 278 K in bulk crystals.
Silicon pixel barrel detector successfully installed in the CMS experiment
Middle of February the upgraded CMS silicon pixel barrel detector has been moved from PSI to CERN and was successfully installed in the CMS experiment.
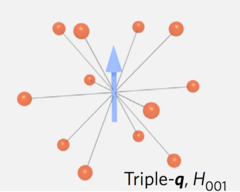
Spiral spin-liquid and the emergence of a vortex-like state in MnSc2S4
Spirals and helices are common motifs of long-range order in magnetic solids, and they may also be organized into more complex emergent structures such as magnetic skyrmions and vortices. A new type of spiral state, the spiral spin-liquid, in which spins fluctuate collectively as spirals, has recently been predicted to exist.
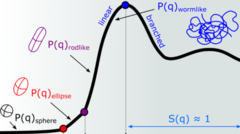
Intermicellar Interactions and the Viscoelasticity of Surfactant Solutions: Complementary Use of SANS and SAXS
In ionic surfactant micelles, basic interactions among distinct parts of surfactant monomers, their counterion, and additives are fundamental to tuning molecular self-assembly and enhancing viscoelasticity. Here, we investigate the addition of sodium salicylate (NaSal) to hexadecyltrimethylammonium chloride and bromide (CTAC and CTAB) and 1-hexadecylpyridinium chloride and bromide (CPyCl and CPyBr), which have distinct counterions and headgroup structures but the same hydrophobic tail.
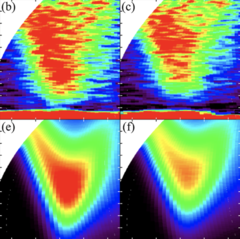
New magnetic phase in the nickelate perovskite TlNiO3
The RNiO3 perovskites are known to order antiferromagnetically below a material-dependent Néel temperature TN. We report experimental evidence indicating the existence of a second magnetically ordered phase in TlNiO3 above TN = 104K, obtained using nuclear magnetic resonance and muon spin rotation spectroscopy.
Magnetic Field Dependence of Excitations Near Spin-Orbital Quantum Criticality
The spinel FeSc2S4 has been proposed to realize a near-critical spin-orbital singlet (SOS) state, where entangled spin and orbital moments fluctuate in a global singlet state on the verge of spin and orbital order.
Probing current-induced magnetic fields in Au|YIG heterostructures with low-energy muon spin spectroscopy
We investigated the depth dependence of current-induced magnetic fields in a bilayer of a normal metal (Au) and a ferrimagnetic insulator (Yttrium Iron Garnet—YIG) by using low energy muon spin spectroscopy (LE-μSR). This allows us to explore how these fields vary from the Au surface down to the buried Au|YIG interface, which is relevant to study physics like the spin-Hall effect.
Full Elasticity Tensor from Thermal Diffuse Scattering
We present a method for the precise determination of the full elasticity tensor from a single crystal diffraction experiment using monochromatic X-rays. For the two benchmark systems calcite and magnesium oxide, we show that the measurement of thermal diffuse scattering in the proximity of Bragg reflections provides accurate values of the complete set of elastic constants.
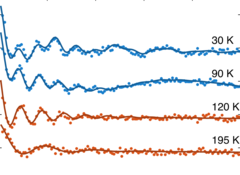
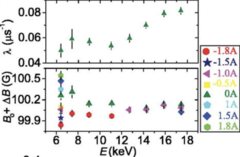
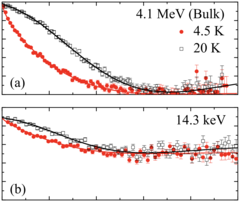
Suppression of magnetic excitations near the surface of the topological Kondo insulator SmB6
We present a detailed investigation of the temperature and depth dependence of the magnetic properties of the three-dimensional topological Kondo insulator SmB6, in particular, near its surface. We find that local magnetic field fluctuations detected in the bulk are suppressed rapidly with decreasing depths, disappearing almost completely at the surface.