NUM division - Publication Highlights
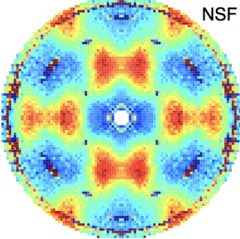
Coulomb spin liquid in anion-disordered pyrochlore Tb2Hf2O7
The charge ordered structure of ions and vacancies characterizing rare-earth pyrochlore oxides serves as a model for the study of geometrically frustrated magnetism. The organization of magnetic ions into networks of corner-sharing tetrahedra gives rise to highly correlated magnetic phases with strong fluctuations, including spin liquids and spin ices. It is an open question how these ground states governed by local rules are affected by disorder.
From golden emperor to filled Buddha
Ancient metal objects are illuminated by neutrons at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI. This enables researchers to discover what is hidden inside them, how they were made and how they can be preserved.
Commissioning and first performance studies of the new CMS pixel detector
In the previous months the new CMS pixel detector was brought into operation. The detector was moved from PSI to CERN and installed in February, followed by an intensive period of commissioning and calibration. This process mostly involved the adjustment of many operational parameters which influence the detector performance, e.g.
The hard worker from Val Mesolcina
For Aldo Antognini, physics and conviviality are in the bloodPSI researcher Aldo Antognini has received more than 2.2 million Swiss francs from the EU for his latest experiment. He wants to find out how magnetism is distributed in the proton. The particle physicist will be able to apply not only his scientific and technical talents, but his social flair as well.
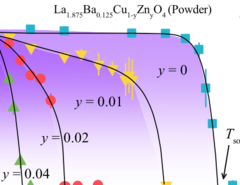
Complementary Response of Static Spin-Stripe Order and Superconductivity to Nonmagnetic Impurities in Cuprates
We report muon-spin rotation and neutron-scattering experiments on nonmagnetic Zn impurity effects on the static spin-stripe order and superconductivity of the La214 cuprates. Remarkably, it was found that, for samples with hole doping x ≈ 1/8, the spin-stripe ordering temperature Tso decreases linearly with Zn doping y and disappears at y ≈ 4%, demonstrating a high sensitivity of static spin-stripe order to impurities within a CuO2 plane.
Equilibrium Skyrmion Lattice Ground State in a Polar Easy-plane Magnet
The skyrmion lattice state (SkL), a crystal built of mesoscopic spin vortices, gains its stability via thermal fluctuations in all bulk skyrmion host materials known to date. Therefore, its existence is limited to a narrow temperature region below the paramagnetic state. This stability range can drastically increase in systems with restricted geometries, such as thin films, interfaces and nanowires.
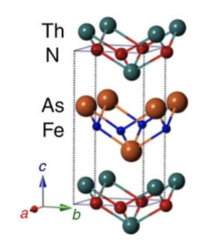
High-Tc superconductivity in undoped ThFeAsN
Unlike the widely studied ReFeAsO series, the newly discovered iron-based superconductor ThFeAsN exhibits a remarkably high critical temperature of 30 K, without chemical doping or external pressure. Here we investigate in detail its magnetic and superconducting properties via muon-spin rotation/relaxation and nuclear magnetic resonance techniques and show that ThFeAsN exhibits strong magnetic fluctuations, suppressed below ≈35 K, but no magnetic order.
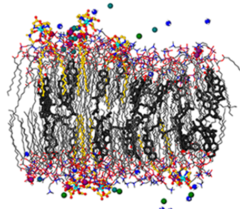
Understanding the Enhanced Magnetic Response of Aminocholesterol Doped Lanthanide-Ion-Chelating Phospholipid Bicelles
Cholesterol (Chol-OH) and its conjugates are powerful molecules for engineering the physicochemical and magnetic properties of phospholipid bilayers in bicelles.
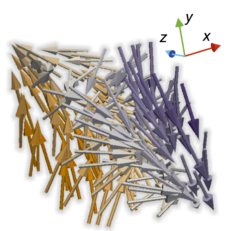
Three-dimensional magnetization structures revealed with X-ray vector nanotomography
In soft ferromagnetic materials, the smoothly varying magnetization leads to the formation of fundamental patterns such as domains, vortices and domain walls. These have been studied extensively in thin films of thicknesses up to around 200 nanometres, in which the magnetization is accessible with current transmission imaging methods that make use of electrons or soft X-rays.