Media Releases
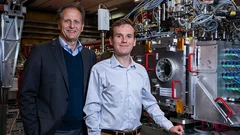
EU grants 14 million to Swiss Researchers
A team with three researchers from the ETH Domain has been awarded a prestigious EU grant. Today, they received the contract signed by the EU confirming the extraordinary 14 million euros funding. With it, they will investigate quantum effects which could become the backbone of future electronics.
Making the impossible possible
Use of multiferroic materials promises more energy-efficient computers because in these, an electric field would suffice to achieve magnetic data storage. Researchers at PSI have now made such a material suitable for computer operating temperatures.
Why the Little Ice Age ended in the middle of the 19th century
In the first half of the 19th century, a series of large volcanic eruptions in the tropics led to a temporary global cooling of Earth's climate. That Alpine glaciers grew and subsequently receded again during the final phase of the so-called Little Ice Age was due to a natural process. This has now been proven by PSI researchers on the basis of ice cores.
This time, it's all bio: SwissFEL makes protein structures visible
For the development of new medicinal agents, accurate knowledge of proteins is crucial. In a pilot experiment, researchers have now, for the first time, used the X-ray free-electron laser SwissFEL of PSI for the examination of protein crystals.
Material from PSI helps to check inconsistencies in the Big Bang theory
Shortly after the Big Bang, radioactive Beryllium-7 atoms were formed, which today, throughout the universe, they have long since decayed. A sample of beryllium-7 artificially produced at PSI has now helped researchers to better understand the first minutes of the universe.
On the path to new high-performance transistors
The electronics industry expects a novel high-performance transistor made of gallium nitride to offer considerable advantages over present-day high-frequency transistors. Yet many fundamental properties of the material remain unknown. Now, for the first time, researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI have observed electrons while they were flowing in this promising transistor. For that they used one of the world's best sources of soft X-rays at PSI's Swiss Light Source SLS.
Cleaner emissions thanks to sponge-like structure
PSI researchers have developed a new catalytic converter for cleaning emissions from natural gas engines. It is very active even at low temperatures and remains that way over a long period of time. This allows natural gas to be burned in a cleaner, more climate-friendly way. Thus natural gas and biogas become more attractive as substitutes for petroleum products – for example, as fuel for cars.
Biological light sensor filmed in action
Using X-ray laser technology, a team led by researchers of the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI has recorded one of the fastest processes in biology. In doing so, they produced a molecular movie that reveals how the light sensor retinal is activated in a protein molecule. Such reactions occur in numerous organisms. The movie shows for the first time how a protein efficiently controls the reaction of the embedded light sensor.
Imaging the inside of injection needles with neutrons
Researchers from the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI, the University of Basel and Roche have used neutron imaging to investigate why cool storage is crucial for syringes pre-filled with a liquid medication.
Light for biomolecules and super-fast processes
The 16th of May is the International Day of Light. The research carried out with light at PSI enables advances in biology and pharmacology and also promotes the development of new materials for data storage and new technologies for personalised medicine.
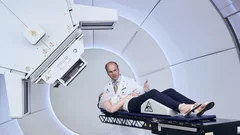
Opening: Advanced technology against cancer
With proton therapy, certain tumours can be irradiated with exceptional precision – while, the surrounding healthy tissue is optimally protected. In Switzerland, this kind of radiation therapy is only possible at PSI. In a joint project with the University Hospital Zurich and the University of Zurich, PSI has expanded its capacity with a state-of-the-art treatment facility: the new, 270-ton Gantry 3.
Cleaner diesel emissions
PSI researchers have found out why it is harder to control the noxious nitrogen oxides in diesel exhaust at low temperatures – and how, in the future, emissions can be cleaned more efficiently depending on the temperature.
Imaging at Paul Scherrer Intitute helps to increase production at ABB site in Aargau
The ABB facility in Wettingen got practical recommendations on increasing production of ceramic components. Researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI examined the components by means of neutron imaging. With the help of these images, ABB employees were able to see where there is still potential for process optimisation. This feasibility study was funded by the Hightech Zentrum Aargau.
Power from nanomagnets
Oles Sendetskyi, winner of a Founder Fellowship at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI, wants to use polarity reversal in nanomagnets to develop a sustainable power source for small devices.
First experiment at SwissFEL carried out successfully
The years of careful planning and construction have paid off: At the newest large-scale research facility of the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI – the X-ray free-electron laser SwissFEL – the first experiment has been carried out successfully. With that, two goals have been achieved: First, a new scientific result is already expected. Second, the interaction of the many individual components of the highly complex facility is being optimised.
More than a prototype
Jean-Baptiste Mosset, winner of a Founder Fellowship at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI, wants to commercialise a neutron detector to spot plutonium and uranium.
Still no sign of dark matter
No evidence of dark matter made of axions – result of an experiment at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI further constrains theories about the nature of dark matter.
A new bio-robot
With a new method for modifying antibodies, Philipp Spycher, winner of a Founder Fellowship at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI, wants to develop drugs that are more stable and, thus, have fewer side-effects.
Atmosphere in X-ray light
PSI researchers have developed an experimental chamber in which they can recreate atmospheric processes and probe them with unprecedented precision, using X-ray light from the Swiss Light Source SLS. In the initial experiments, they have studied the production of bromine, which plays an essential role in the decomposition of ozone in the lower layers of the atmosphere. In the future, the new experiment chamber will also be available for use by researchers from other scientific fields.
More than just spilling the beans
Because of their high nitrogen content, spent coffee grounds are a popular garden fertilizer. Recycled in this manner, they already contribute to an environmentally friendly waste management. But they have the potential to deliver much more: a new procedure developed at the PSI allows high quality methane to be formed from spent coffee grounds. PSI researchers involved in a pilot project carried out in cooperation with the Swiss food producer Nestlé were able to show that spent coffee grounds left over during the production of instant coffee can be efficiently re-used elsewhere.