Health Innovation
In the area of Health Innovation, several research groups at PSI are engaged in the study of fundamental questions regarding biology and cancer therapy. For example, they explore the structure of proteins – extremely complex biomolecules that are responsible for many different functions in organisms. Using PSI’s large research facilities, scientists also explore processes in biological tissue in order to fully understand their function and the development of specific diseases or deterioration processes. The ultimate goal is to find medicines that allow people to live as healthy a life as possible.
Patients with specific types of cancer are treated at the proton therapy facility on the PSI campus. Radiopharmaceuticals provide cancer treatments for very small tumours distributed throughout the body.
Find out more at: Overview Health Innovation
Investigation of a new method for the diagnosis of cancer in breast tissue
The Paul Scherrer Institute PSI has developed a new breast cancer diagnostic method, and is now carrying out first tests on non-preserved human tissue in conjunction with Kantonsspital Baden AG. This new method should be able to reveal structures that cannot be seen using conventional mammography. Scientists from the research department at Philips are currently investigating the use of this process as the basis for application in medical practice.
X-ray methods help to understand brain disorders better
An international team of researchers has developed a new method for making detailed X-ray images of brain tissue, which has been used to make the myelin sheaths of nerve fibres visible. Damage to these protective sheaths can lead to various disorders, such as multiple sclerosis. The facility for creating these images of the protective sheaths of nerve cells is being operated at the Swiss Light Source (SLS), at the Paul Scherrer Institute.
Dem Rätsel der Centriolen-Bildung auf der Spur
In menschlichen Zellen finden sich stammesgeschichtlich sehr alte Funktionseinheiten, die als Centriolen bezeichnet werden. Ein Forscherteam vom PSI und der ETH Lausanne hat nun erstmals ein Modell für die Bildung der Centriolen vorgestellt. Das erstaunende Ergebnis ist, dass die Neuner-Symmetrie des Centriols durch die Fähigkeit eines einzelnen Proteins sich selbst zu organisieren zustande kommt.This news release is only available in French and German.
Effizienter Gentransfer nun auch in Säugerzellen möglich
Wissenschaftler am Paul Scherrer Institut entwickelten ein neues Verfahren, das auch zur Entwicklung von neuen Medikamenten genutzt werden kann.Die Gentechnik ist aus der modernen Biologie nicht mehr wegzudenken. Sie liefert Werkzeuge, mit denen Forscher Gene aus dem Erbgut von Zellen herausschneiden, verändern und einfügen können. Die stabile Einführung mehrerer Gene in Säugetierzellen gilt zwar als Schlüsseltechnologie, die verfügbaren Methoden waren bislang aber äusserst ineffizient. Wissenschaftler am PSI haben nun eine neuartige Technik entwickelt.This news release is only available in German.
25 Jahre erfolgreiche Behandlung von Augentumoren am PSI
Heute haben die Physiker und Ärzte des PSI diesen Erfolg mit einem Festsymposium gefeiert. In Anwesenheit von geladenen Gästen aus Forschung, Medizin und Politik wurde dabei auch die brandneue Behandlungsanlage OPTIS 2 eingeweiht. Diese Bestrahlungseinrichtung befindet sich nicht nur technisch auf dem allerneusten Stand, sondern überzeugt auch durch ihre Patientenfreundlichkeit.This news release is only available in German.
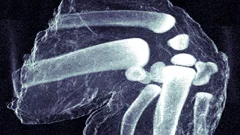
High-resolution method for computed nano-tomography developed
High-resolution method for computed nano-tomography developedA novel nano-tomography method developed by a team of researchers from the Technische Universität München, the Paul Scherrer Institute and the ETH Zurich opens the door to computed tomography examinations of minute structures at nanometer resolutions. The new method makes possible, for example, three-dimensional internal imaging of fragile bone structures.
New X-ray technique distinguishes between that which previously looked the same
Images generated using the phase-contrast technique allow one to distinguish between tissue types such as muscle, cartilage, tendons or soft-tissue tumours that look virtually identical in conventional X-ray images. Researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute and the Chinese Academy of Science have further developed the technique to make it easier to use in the future. This could help in the detection of tumours or in the identification of hazardous objects in luggage.
Paul Scherrer Institut ermöglicht bessere Versorgung der Spitäler mit hochwirksamem Krebsmedikament
Das Paul Scherrer Institut ist für die Behandlung von bestimmten Krebserkrankungen mittels seiner einzigartigen Protonentherapie-Anlage bekannt. Nun hilft das PSI auch bei der Behandlung einer Gruppe von Krebspatienten durch die Herstellung eines Krebsmedikaments. Die erste Patientendosis wurde heute am Zentrum für Radiopharmazeutische Wissenschaften des PSI hergestellt und im Kantonsspital Luzern einem Patienten verabreicht.This news release is only available in German.
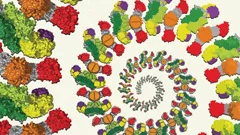
Attacking the lifeline of tumour cells
Researchers at Biomedicum Helsinki, Finland, and the Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI) in Villigen, Switzerland, have determined the crystal structure of the ligand-binding domain of a vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor in complex with one of its ligands (VEGF-C).
Ticket für die Reise durch die Zelle
Publikation in Cell. Forscher entdecken Mechanismus für wesentliche Erkennungsvorgänge in lebenden Zellen. Über ihre Ergebnisse berichten die Forscher in der neuesten Ausgabe der Fachzeitschrift Cell.This news release is only available in German.
Komplexe in den Griff bekommen
Die meisten Vorgänge in lebenden Zellen werden von molekularen Maschinen aus vielen Proteinen ausgeführt. Wissenschaftler von PSI und EMBL haben ein automatisiertes Verfahren zur Herstellung von solchen Multiprotein-Komplexen für die Forschung entwickelt.This news release is only available in German.
Röntgenbilder mit Durchblick
Der Nationale Latsis-Preis 2008 geht an Franz Pfeiffer. Der Physiker hat einen Weg gefunden, die in der Spitzenforschung angewandten Verfahren der Röntgentechnik auch für gewöhnliche Röntgengeräte nutzbar zu machen. Der mit 100'000 Franken dotierte Preis wird jährlich vom Schweizerischen Nationalfonds (SNF) im Auftrag der Latsis-Stiftung vergeben.This news release is only available in German.
Promising targets for drug development
ETH Researchers determine atomic structure of the mammalian fatty acid factory. Mammalian fatty acid synthase is one of the most complex molecular synthetic machines in human cells. It is a promising target for the development of anti-cancer and anti-obesity drugs and for the treatment of metabolic disorders. Researchers of ETH Zurich have determined the atomic structure of a mammalian fatty acid synthase.
Vitamin B12 ist das Trojanische Pferd der Krebsforscher am schweizerischen Zentrum für radiopharmazeutische Wissenschaft
Erste Klinische Studie soll Mitte Juni beginnen.This news release is only available in German.
Scharfe Röntgenbilder im Krankenhaus und am Flughafen
Publication in Nature. Researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI) and the EPFL in Switzerland have developed a novel method for producing dark-field X-ray images at wavelengths used in typical medical and industrial imaging equipment. Dark-field images provide more detail than ordinary X-ray radiographs and could be used to diagnose the onset of osteoporosis, breast cancer or Alzheimer's disease, to identify explosives in hand luggage, or to pinpoint hairline cracks or corrosion in functional structures.