NUM division - Publication Highlights
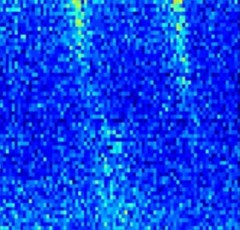
Frequency-Induced Bulk Magnetic Domain-Wall Freezing Visualized by Neutron Dark-Field Imaging
We use neutron dark-field imaging to visualize and interpret the response of bulk magnetic domain walls to static and dynamic magnetic excitations in (110)-Goss textured iron silicon high-permeability steel alloy. We investigate the domain-wall motion under the influence of an external alternating sinusoidal magnetic field.
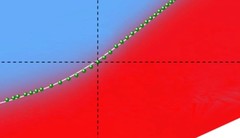
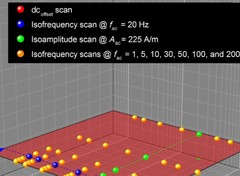
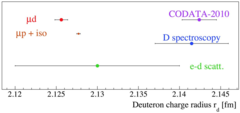
Laser spectroscopy of muonic deuterium
The deuteron is the simplest compound nucleus, composed of one proton and one neutron. Deuteron properties such as the root-mean-square charge radius rd and the polarizability serve as important benchmarks for understanding the nuclear forces and structure. Muonic deuterium μd is the exotic atom formed by a deuteron and a negative muon μ-.
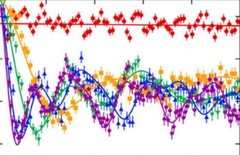
Search for the lepton flavour violating decay μ+→e+γ with the full dataset of the MEG experiment
The final results of the search for the lepton flavour violating decay μ+→e+γ based on the full dataset collected by the MEG experiment at the Paul Scherrer Institut in the period 2009–2013 and totalling 7.5×1014 stopped muons on target are presented.
Coexisting multiple order parameters in single-layer LuMnO3 films
Magnetoelectric multiferroics hold great promise for electrical control of magnetism or magnetic control of ferroelectricity. However, single phase ferroelectric materials with a sizeable ferromagnetic magnetization are rare. Here, we demonstrate that a single-phase orthorhombic LuMnO3 thin film features coexisting magnetic and ferroelectric orders.
Volume-wise destruction of the antiferromagnetic Mott insulating state through quantum tuning
RENiO3 (RE=rare-earth element) and V2O3 are archetypal Mott insulator systems. When tuned by chemical substitution (RENiO3) or pressure (V2O3), they exhibit a quantum phase transition (QPT) between an antiferromagnetic Mott insulating state and a paramagnetic metallic state. Because novel physics often appears near a Mott QPT, the details of this transition, such as whether it is first or second order, are important.
On the Interaction between Digitonin and Cholesterol in Langmuir Monolayers
In this article, we describe the effect of a highly hemolytic saponin, digitonin, on model lipids cholesterol and dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (DPPC) using a combination of tensiometric (surface pressure and dilatational surface elasticity), spectroscopic (infrared reflection absorption spectroscopy, IRRAS), microscopic (fluorescence microscopy), and scattering techniques (neutron reflectivity, NR, and grazing incidence X-ray diffraction, GIXD).
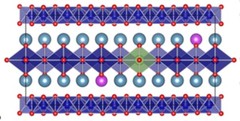
Phononic Structure Engineering: the Realization of Einstein Rattling in Calcium Cobaltate for the Suppression of Thermal Conductivity
Phonons in condensed matter materials transmit energy through atomic lattices as coherent vibrational waves. Like electronic and photonic properties, an improved understanding of phononic properties is essential for the development of functional materials, including thermoelectric materials. Recently, an Einstein rattling mode was found in thermoelectric material Na0.8CoO2, due to the large displacement of Na between the [CoO2] layers.
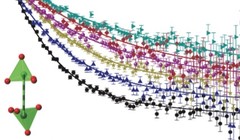
Physical realization of a quantum spin liquid based on a complex frustration mechanism
Unlike conventional magnets where the magnetic moments are partially or completely static in the ground state, in a quantum spin liquid they remain in collective motion down to the lowest temperatures. The importance of this state is that it is coherent and highly entangled without breaking local symmetries.
Iridates from the molecular side
New exotic phenomena have recently been discovered in oxides of paramagnetic Ir4+ ions, widely known as ‘iridates’. Their remarkable properties originate from concerted effects of the crystal field, magnetic interactions and strong spin-orbit coupling, characteristic of 5d metal ions.
![Sketch of a ferroic triangle showing the relation and techniques with which the ferroic orders, FM, AFM, and FE, and their mutual coupling have been established. The experimental techniques written in black letters (polarized neutron reflectometry, PNR; resonant soft x-ray diffraction, SXRD; x-ray diffraction, XRD) to identify ferroic properties have been reported elsewhere [22, 24]. Magnetization, susceptibility, μSR, neutron diffraction, and electrical polarization are reported.](/sites/default/files/styles/primer_teaser_square_scale/public/import/num/SHL20160822CoexistingEN/CWS_PRB_94_054423_2016.jpg?itok=fIYHS3v6)