Scientific Highlights
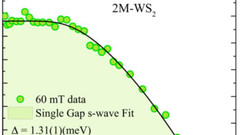
Nodeless superconductivity and its evolution with pressure in the layered dirac semimetal 2M-WS2
Recently, the transition metal dichalcogenide (TMD) system 2M-WS2 has been identified as a Dirac semimetal exhibiting both superconductivity with the highest Tc ~ 8.5 K among all the TMD materials and topological surface states. Here we report on muon spin rotation (μSR) and density functional theory studies of microscopic SC properties and the electronic structure in 2M-WS2 at ambient and under hydrostatic pressures (pmax = 1.9 GPa).
Bulk single-crystal growth of the theoretically predicted magnetic Weyl semimetals RAlGe (R = Pr, Ce)
We explore two methods for single-crystal growth of the theoretically proposed magnetic Weyl semimetals RAlGe (R = Pr, Ce), which prove that a floating-zone technique, being both crucible- and flux-free, is crucial to obtain perfectly stoichiometric RAlGe crystals. In contrast, the crystals grown by a flux-growth technique tend to be Al-rich. We further present both structural and elemental analyses, along with bulk magnetization and electrical resistivity data on the crystals prepared by the floating-zone technique. Both systems with the intended 1:1:1 stoichiometry crystallize in the anticipated polar I41md (No. 109) space group, although neither displays the theoretically expected ferromagnetic ground state.
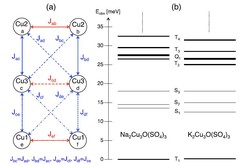
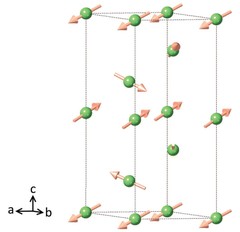
Spin triplet ground-state in the copper hexamer compounds A2Cu3O(SO4)3 (A = Na, K)
The compounds A2Cu3O(SO4)3(A=Na,K) are characterized by copper hexamers which are weakly coupled along the b axis to realize one-dimensional antiferromagnetic chains below TN≈3K, whereas the interchain interactions along the a and c axes are negligible. We investigated the energy-level splittings of the copper hexamers by inelastic neutron scattering below and above TN.
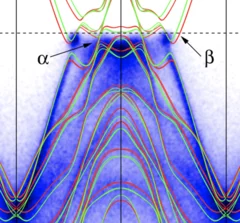
Evidence of a Coulomb-Interaction-Induced Lifshitz Transition and Robust Hybrid Weyl Semimetal in Td-MoTe2
Using soft x-ray angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy we probed the bulk electronic structure of Td-MoTe2. We found that on-site Coulomb interaction leads to a Lifshitz transition, which is essential for a precise description of the electronic structure. A hybrid Weyl semimetal state with a pair of energy bands touching at both type-I and type-II Weyl nodes is indicated by comparing the experimental data with theoretical calculations.
Pauling Entropy, Metastability, and Equilibrium in Dy2Ti2O7 Spin Ice
Determining the fate of the Pauling entropy in the classical spin ice material Dy2Ti2O7 with respect to the third law of thermodynamics has become an important test case for understanding the existence and stability of ice-rule states in general. The standard model of spin ice—the dipolar spin ice model—predicts an ordering transition at T ≈ 0.15K, but recent experiments by Pomaranski et al.
Revisiting the magnetic structure of La1/3Sr2/3FeO3 by neutron powder diffraction and Mössbauer spectroscopy
La1/3Sr2/3FeO3 is reported to show a 2Fe4+ → Fe3+ + Fe5+ charge disproportionation (CD) accompanied by Fe3+/Fe5+ charge ordering (CO) and a metal-insulator (MI) transition at 200 K [1]. The MI transition was ascribed to CD and CO. Based on the CO, the magnetic structure was reported to be P-3m1 or P1 from the neutron diffraction studies performed at 50 K and 15 K, respectively [2]. The former seems not to be a correct solution since the presence of rotoinversion -3 is incompatible with the claimed collinear magnetic structure, with the collinear moments in the ab-plane in R-3c metric; and the latter might be a correct solution, but without any symmetry restrictions in space group P1.
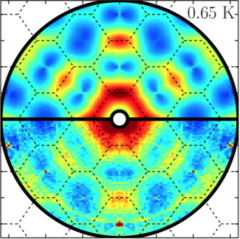
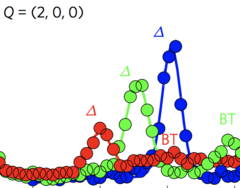
4-spin plaquette singlet state in the Shastry–Sutherland compound SrCu2(BO3)2
The study of interacting spin systems is of fundamental importance for modern condensed-matter physics. On frustrated lattices, magnetic exchange interactions cannot be simultaneously satisfied, and often give rise to competing exotic ground states. The frustrated two-dimensional Shastry–Sutherland lattice realized by SrCu2(BO3)2 is an important test to our understanding of quantum magnetism.