Laboratory for Neutron and Muon Instrumentation (LIN)

Through a unique mix of technical and scientific staff the Laboratory for Neutron and Muon Instrumentation (LIN) is central to the operation and development of scientific instrumentation and methods for the SINQ and UCN neutron sources as well as the SμS muon source at the Paul Scherrer Institut (PSI). These efforts enable both PSI researchers as well as the international scientific user community to carry out state-of-the-art experiments that employ neutron and muon particle beams to solve topical scientific issues in fields ranging from particle physics to solid state physics to materials science.
Lab News & Scientific Highlights
Dichotomous Electrons: Travelling without Moving
Neutron scattering experiments give new understanding of how localized and free-flowing electrons collaborate to create material functionality.
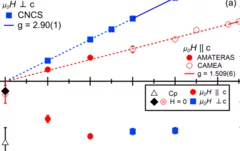
Field-tuned quantum renormalization of spin dynamics in the honeycomb lattice Heisenberg antiferromagnet YbCl3
The basis for our understanding of quantum magnetism has been the study of elegantly simple model systems. However, even for the antiferromagnetic honeycomb lattice with isotropic spin interactions – one of the simplest model systems – a detailed understanding of quantum effects is still lacking. Here, using inelastic neutron scattering measurements of the honeycomb lattice material YbCl3, we elucidate how quantum effects renormalize ...
Swiss precision optics in Sweden
PSI has finalized the precision Selene neutron optics for the ESTIA instrument. The complex state-of-the-art guide was installed at the European Spallation Source as a Swiss in-kind delivery.